UTI St. John, also known as urinary tract infection St. John, is a common bacterial infection that affects the urinary tract, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. It is a painful and uncomfortable condition that can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for UTI St. John.
Symptoms of UTI St. John:
UTI St. John The symptoms of UTI St. John may vary depending on the affected area of the urinary tract. However, some of the most common symptoms include:
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urge to urinate, even when the bladder is empty
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Blood in urine
- Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or back
- Fever or chills (in severe cases)
Causes of UTI St. John:
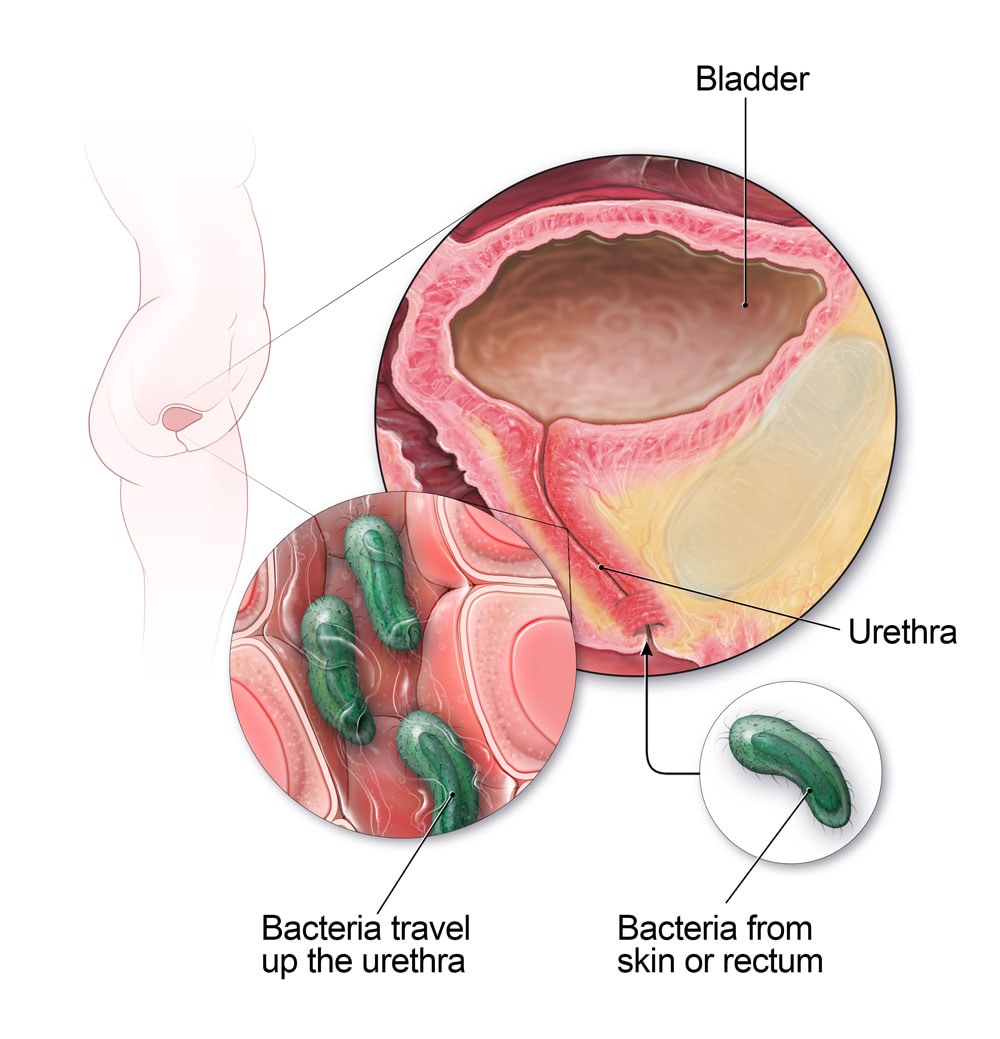
UTI St. John is caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. The bacteria can enter the urinary tract through the urethra and cause infection. Women are more prone to UTIs than men due to the shorter length of their urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
Other risk factors for UTI St. John include:
- Sexual activity
- Menopause
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes
- Use of certain birth control methods, such as diaphragms and spermicides
- Urinary tract abnormalities
- Weak immune system
- Catheterization
Diagnosis of UTI St. John:
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Your doctor will perform a physical examination and ask for a urine sample to check for the presence of bacteria and white blood cells. In some cases, imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan may be necessary to identify any abnormalities in the urinary tract.
Treatment of UTI St. John:
The treatment for UTI St. John usually involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The type of antibiotic prescribed may depend on the severity of the infection and the bacteria responsible. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor, even if you start feeling better before the medication is finished.
Along with antibiotics, your doctor may also recommend pain relievers to ease the discomfort and burning sensation during urination. Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help flush out the bacteria from the urinary tract and prevent further infections.
Prevention of UTI St. John:
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of getting UTI St. John:
- Drink plenty of water and fluids to stay hydrated and flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Urinate frequently, and make sure to empty your bladder completely.
- Wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from the anus from entering the urethra.
- Avoid using douches, scented feminine products, and harsh soaps in the genital area, as they can irritate the urethra and increase the risk of infection.
- Urinate after sexual activity to flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urethra during intercourse.
- Use condoms during sexual activity to reduce the risk of transmitting bacteria.
- Avoid holding your urine for extended periods, as this can allow bacteria to multiply in the urinary tract.
In conclusion, UTI St. John is a common bacterial infection that can cause discomfort and pain in the urinary tract. It is essential to seek medical attention if you
UTI St.John How Its Work?
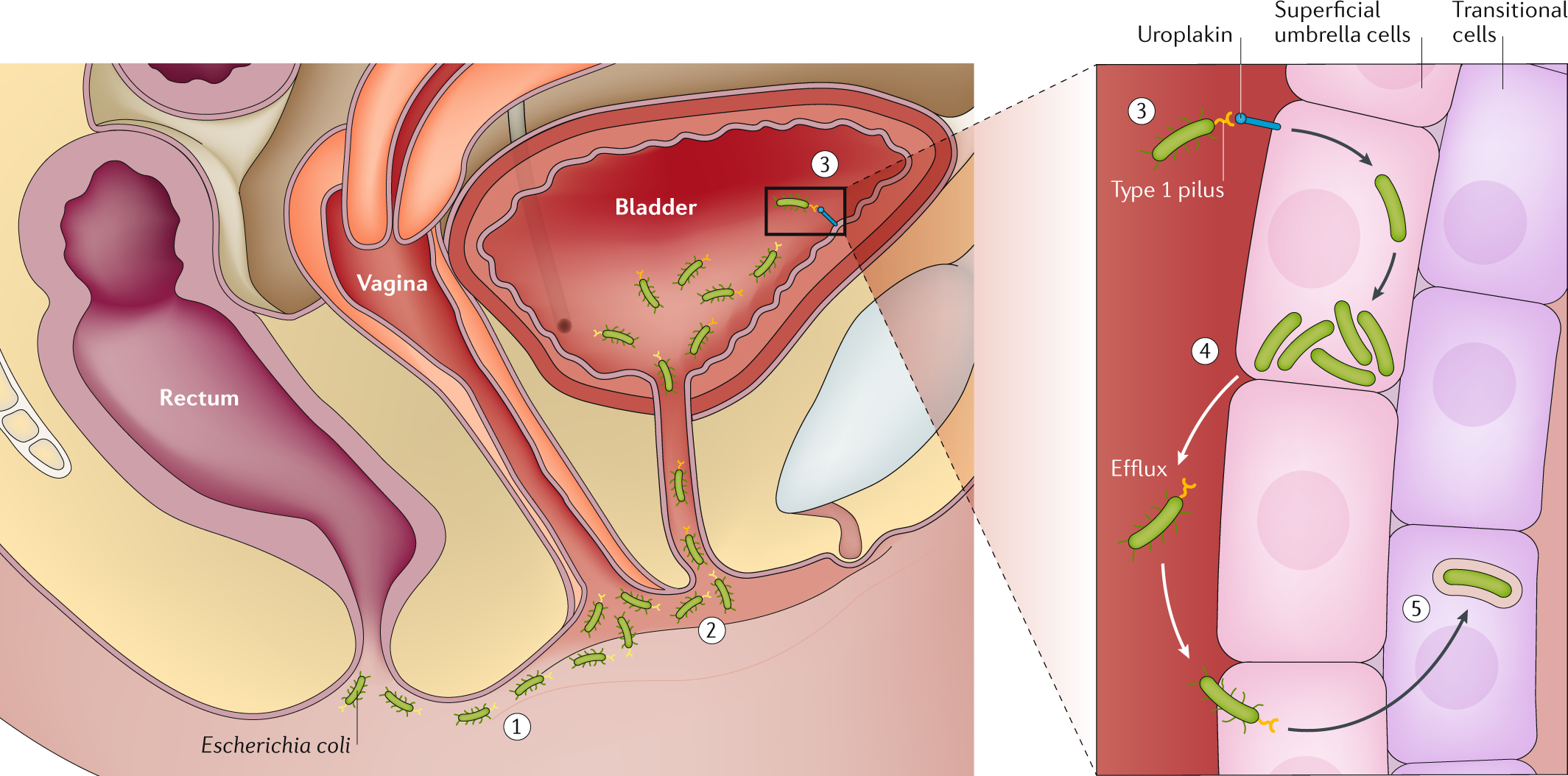
UTI St. John, or urinary tract infection St. John, is a bacterial infection that affects the urinary tract. It is caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. The bacteria can enter the urinary tract through the urethra and cause an infection.
The urinary tract consists of several organs that work together to remove waste products from the body. The organs include the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste products from the blood and produce urine, which is then transported through the ureters to the bladder. The bladder stores the urine until it is ready to be eliminated from the body through the urethra.
When bacteria enter the urinary tract, they can attach to the lining of the bladder or urethra and start to multiply. This can cause inflammation and irritation, leading to symptoms such as pain or burning during urination, frequent urge to urinate, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or back.
If left untreated, the infection can spread to the kidneys and cause more severe symptoms such as fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. In severe cases, UTI St. John can lead to kidney damage or sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
To diagnose UTI St. John, a doctor will perform a physical examination and ask for a urine sample to check for the presence of bacteria and white blood cells. Imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan may also be necessary to identify any abnormalities in the urinary tract.
Conclusion:
Treatment for UTI St. John usually involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The type of antibiotic prescribed may depend on the severity of the infection and the bacteria responsible. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor, even if you start feeling better before the medication is finished.
Along with antibiotics, your doctor may also recommend pain relievers to ease the discomfort and burning sensation during urination. Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help flush out the bacteria from the urinary tract and prevent further infections.
In conclusion, UTI St. John is a bacterial infection that affects the urinary tract. It is caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can enter the urinary tract through the urethra and cause inflammation and irritation. Treatment usually involves antibiotics and pain relievers, along with measures to prevent further infections. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of UTI St. John to prevent serious health complications.























