
I. Introduction
Obesity is a growing epidemic that plagues societies worldwide. It transcends age, gender, and socioeconomic boundaries, affecting millions of people. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the multifaceted aspects of obesity, from its causes and health implications to prevention strategies and government initiatives.
Table of Contents
- I. Introduction
- A. Definition and Prevalence
- B. Significance of the Issue
- C. The Global Perspective
- II. Causes of Obesity
- A. Genetic Factors
- 1. Role of Genetics
- 2. Family History
- B. Environmental Factors
- 1. Sedentary Lifestyle
- 2. Diet and Nutrition
- 3. Socioeconomic Influence
- C. Psychological Factors
- 1. Emotional Eating
- 2. Stress and Obesity
- 3. Behavioral Patterns
- III. Health Implications
- A. Physical Health
- 1. Cardiovascular Diseases
- 2. Type 2 Diabetes
- 3. Joint Problems
- B. Mental Health
- 1. Depression
- 2. Anxiety
- 3. Low Self-Esteem
- IV. Childhood Obesity
- A. The Alarming Rise
- B. Factors Contributing to Childhood Obesity
- 1. Lack of Physical Activity
- 2. Unhealthy Diets
- 3. Parental Influence
- C. Long-term Consequences
- V. Obesity and Society
- A. Stigmatization and Discrimination
- B. Economic Burden
- C. Media Influence
- 1. Advertising
- 2. Body Image
- VI. Obesity Prevention
- A. Healthy Diet
- 1. Balanced Nutrition
- 2. Portion Control
- B. Regular Physical Activity
- 1. Exercise Regimens
- 2. Lifestyle Changes
- C. Education and Awareness
- 1. School Programs
- 2. Community Initiatives
- VII. Medical Treatments
- A. Diet and Exercise Programs
- 1. Medical Supervision
- 2. Success Rates
- B. Pharmacotherapy
- 1. Medications for Obesity
- 2. Side Effects
- C. Bariatric Surgery
- 1. Types of Surgery
- 2. Eligibility Criteria
- VIII. Psychological Interventions
- A. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- B. Mindfulness-Based Approaches
- C. Support Groups
- IX. Obesity in Adulthood
- A. Challenges in Weight Loss
- B. Metabolic Changes
- C. Maintaining Weight Loss
- X. Government Initiatives
- A. Policies and Regulations
- B. Sugar Tax
- C. School Lunch Programs
- XI. The Future of Obesity
- A. Emerging Research
- B. Technological Solutions
- C. Genetics and Personalized Medicine
- XII. Case Studies
- A. Real-life Stories of Overcoming Obesity
- B. Notable Success Stories
- XIII. Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
I Investigated the Most Obese City in America…
A. Definition and Prevalence
Obesity is not simply a matter of carrying excess weight; it is a complex medical condition characterized by the accumulation of excessive body fat. To diagnose obesity, healthcare professionals often use the Body Mass Index (BMI), which measures an individual’s weight in relation to their height. Generally, a BMI of 30 or higher indicates obesity.
The prevalence of obesity has surged dramatically in recent decades. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that obesity rates worldwide have tripled since 1975. In 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight, and out of these, over 650 million were obese. These numbers emphasize the importance of dealing with this problem promptly.
B. Significance of the Issue
Obesity is not merely a cosmetic concern; it is a significant public health problem with far-reaching consequences. It is associated with a myriad of serious health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Moreover, it can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental well-being, leading to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
C. The Global Perspective
Obesity is a global health concern that transcends borders. It is not confined to developed nations; it is prevalent in low- and middle-income countries as well. This global perspective underscores the need for coordinated efforts to combat the obesity epidemic.
II. Causes of Obesity
Understanding the causes of obesity is crucial for devising effective prevention and intervention strategies. Obesity is a multifactorial condition with various contributing factors, including genetic, environmental, and psychological elements.
A. Genetic Factors
1. Role of Genetics
Genetics plays a role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to obesity. Some people may have a genetic predisposition that makes them more likely to gain weight.
2. Family History
Family history can be a significant factor. If an individual has close relatives who are obese, they may be at a higher risk themselves.
B. Environmental Factors
1. Sedentary Lifestyle
Modern life often promotes sedentary behaviors. With the prevalence of desk jobs, increased screen time, and reduced physical activity, many people lead sedentary lifestyles, which contribute to obesity.
2. Diet and Nutrition
Dietary choices are a primary driver of obesity. Consuming high-calorie, low-nutrient foods, often referred to as “junk food,” can lead to weight gain over time.
3. Socioeconomic Influence
Socioeconomic status can also influence obesity rates. Individuals with lower incomes may have limited access to healthy food options and recreational facilities, making it more challenging to maintain a healthy weight.
C. Psychological Factors
1. Emotional Eating
Emotional factors can play a significant role in obesity. Certain people seek solace in food when they are stressed, feeling down, or bored, which often results in excessive eating.
2. Stress and Obesity
Persistent stress can trigger hormonal fluctuations that encourage the accumulation of excess weight. Stress may also contribute to unhealthy coping mechanisms like binge eating.
3. Behavioral Patterns
Behavioral patterns, such as eating out of habit or eating late at night, can contribute to weight gain. These habits can be challenging to break without intervention.
 Color illustration causes and effects of obesity vector illustration
Color illustration causes and effects of obesity vector illustration
III. Health Implications
Obesity has far-reaching health implications, affecting nearly every system in the body. From cardiovascular problems to mental health issues, the consequences of obesity are severe and multifaceted.
A. Physical Health
1. Cardiovascular Diseases
Obesity is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke. Excess body fat can lead to the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of blockages and heart attacks.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is strongly associated with obesity. Excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels.
3. Joint Problems
The excess weight carried by obese individuals puts added stress on the joints, particularly those in the lower body. This can result in health conditions such as osteoarthritis and persistent joint discomfort.
B. Mental Health
1. Depression
Obesity and depression often go hand in hand. The stigma and discrimination faced by obese individuals can contribute to feelings of isolation and sadness.
2. Anxiety
Anxiety disorders are more common among individuals with obesity. The psychological burden of obesity can lead to heightened anxiety levels.
3. Low Self-Esteem
Obesity can erode an individual’s self-esteem. Negative body image and societal pressure to conform to certain beauty standards can lead to low self-worth.
IV. Childhood Obesity
Childhood obesity is a particular cause for concern, as it sets the stage for a lifetime of health challenges. Understanding the factors contributing to childhood obesity is essential for prevention.
A. The Alarming Rise
Childhood obesity rates have risen dramatically in recent years. This trend is deeply concerning, as obese children are more likely to become obese adults.
B. Factors Contributing to Childhood Obesity
1. Lack of Physical Activity
Many children today have limited opportunities for physical activity. Factors such as excessive screen time and reduced physical education in schools contribute to this issue.
2. Unhealthy Diets
Children are exposed to high-calorie, low-nutrient foods from a young age, which can set unhealthy dietary habits for life.
3. Parental Influence
Parents play a crucial role in shaping a child’s eating habits and physical activity levels. Lack of parental awareness and education can contribute to childhood obesity.
C. Long-term Consequences
Childhood obesity can lead to a host of health problems, including a higher risk of obesity-related diseases in adulthood. Additionally, obese children may face social and psychological challenges.
V. Obesity and Society
Obesity extends beyond the individual level and has profound effects on society as a whole. Understanding the societal implications of obesity is essential for addressing this issue effectively.
A. Stigmatization and Discrimination
Obese individuals often face stigma and discrimination in various aspects of life, from employment opportunities to interpersonal relationships.
B. Economic Burden
The economic costs of obesity are substantial. Healthcare expenditures related to obesity and its associated conditions are a significant burden on healthcare systems.
C. Media Influence
The media plays a pivotal role in shaping societal attitudes towards body image and weight. Understanding how media influences perceptions of obesity is crucial.
1. Advertising
Advertising often promotes unhealthy food choices and unrealistic body standards, contributing to the obesity epidemic.
2. Body Image
Media portrayals of idealized body images can lead to unrealistic expectations and body dissatisfaction among individuals.
VI. Obesity Prevention
Preventing obesity requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses lifestyle changes, education, and community involvement. Effective prevention strategies can help reduce the burden of obesity.
A. Healthy Diet
1. Balanced Nutrition
Promoting balanced nutrition is essential for preventing obesity. Educating individuals about the importance of a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is crucial.
2. Portion Control
Controlling portion sizes can help individuals avoid overeating. Understanding appropriate portion sizes is a valuable skill for weight management.
B. Regular Physical Activity
1. Exercise Regimens
Engaging in regular exercise is a cornerstone of obesity prevention. Developing exercise regimens that are enjoyable and sustainable is key.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Encouraging lifestyle changes, such as walking or cycling for transportation and incorporating physical activity into daily routines, can promote long-term fitness.
C. Education and Awareness
1. School Programs
Schools can play a vital role in obesity prevention by incorporating nutrition education and physical activity into their curricula.
2. Community Initiatives
Community-based programs and initiatives can raise awareness about obesity and provide resources and support for individuals looking to make healthier choices.
 Smiling woman with overweight in a tracksuit doing exercises on a sports field in a park
Smiling woman with overweight in a tracksuit doing exercises on a sports field in a park
VII. Medical Treatments
While prevention is the ideal approach to obesity, medical treatments may be necessary for individuals who are already obese. These treatments aim to assist with weight loss and improve overall health.
A. Diet and Exercise Programs
1. Medical Supervision
Some individuals may benefit from medically supervised diet and exercise programs, which provide tailored guidance and support.
2. Success Rates
Understanding the success rates of different diet and exercise programs is essential for individuals considering these options.
B. Pharmacotherapy
1. Medications for Obesity
Certain medications can aid in weight loss by reducing appetite or altering the absorption of nutrients.
2. Side Effects
It’s important to be aware of the potential side effects of obesity medications and weigh the risks and benefits.
C. Bariatric Surgery
1. Types of Surgery
Bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, is a surgical option for weight loss.
2. Eligibility Criteria
Not everyone is eligible for bariatric surgery. Understanding the criteria for candidacy is crucial.
VIII. Psychological Interventions
Obesity is not solely a physical issue; it often has psychological underpinnings. Psychological interventions can help individuals address the emotional aspects of obesity.
A. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a widely used approach for treating obesity. It helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to food and eating.
B. Mindfulness-Based Approaches
Mindfulness practices can help individuals develop a healthier relationship with food by promoting awareness of eating habits and emotional triggers.
C. Support Groups
Support groups provide a sense of community and understanding for individuals dealing with obesity. They can be instrumental in providing encouragement and motivation.
 Photo by AllGo – An App For Plus Size People on Unsplash
Photo by AllGo – An App For Plus Size People on Unsplash
IX. Obesity in Adulthood
Obesity in adulthood presents unique challenges. Weight loss can be more difficult, and metabolic changes may occur, affecting overall health.
A. Challenges in Weight Loss
Adults often face additional challenges in losing weight, such as hormonal changes and lifestyle factors.
B. Metabolic Changes
Obesity can lead to metabolic changes that affect how the body processes food and stores fat. Understanding these changes is crucial for managing obesity in adulthood.
C. Maintaining Weight Loss
Maintaining weight loss is often more challenging than losing weight initially. Strategies for long-term weight management are essential.
X. Government Initiatives
Governments play a pivotal role in addressing the obesity epidemic through policies and regulations that promote healthier lifestyles.
A. Policies and Regulations
Governments can implement policies that regulate food advertising, labeling, and access to unhealthy foods.
B. Sugar Tax
Sugar taxes on sugary beverages have been implemented in some regions as a means of reducing sugar consumption and obesity rates.
C. School Lunch Programs
Schools can contribute to obesity prevention by offering nutritious and balanced meals to students.
 Image by rawpixel.com on Freepik
Image by rawpixel.com on Freepik
XI. The Future of Obesity
As science and technology continue to advance, new approaches to tackling obesity emerge. The future holds promise for innovative solutions to this pervasive issue.
A. Emerging Research
Ongoing research in genetics, metabolism, and behavioral science provides insights into the underlying causes of obesity and potential treatments.
B. Technological Solutions
Technological advancements, such as wearable fitness trackers and mobile health apps, offer new tools for managing obesity and promoting healthier lifestyles.
C. Genetics and Personalized Medicine
Understanding an individual’s genetic predisposition to obesity can lead to personalized treatment approaches that are more effective.
XII. Case Studies
Real-life stories of individuals who have successfully overcome obesity can provide inspiration and practical insights into weight management.
A. Real-life Stories of Overcoming Obesity
Highlighting individuals who have achieved significant weight loss and improved health can offer hope and motivation to others.
B. Notable Success Stories
Examining notable success stories in the realm of obesity treatment and prevention can shed light on effective strategies and interventions.
XIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, obesity is a complex and pervasive issue with far-reaching implications for individuals and society as a whole. Addressing obesity requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses prevention, medical treatments, psychological interventions, and government initiatives. By understanding the causes and consequences of obesity and implementing effective strategies, we can work toward a healthier future for all.
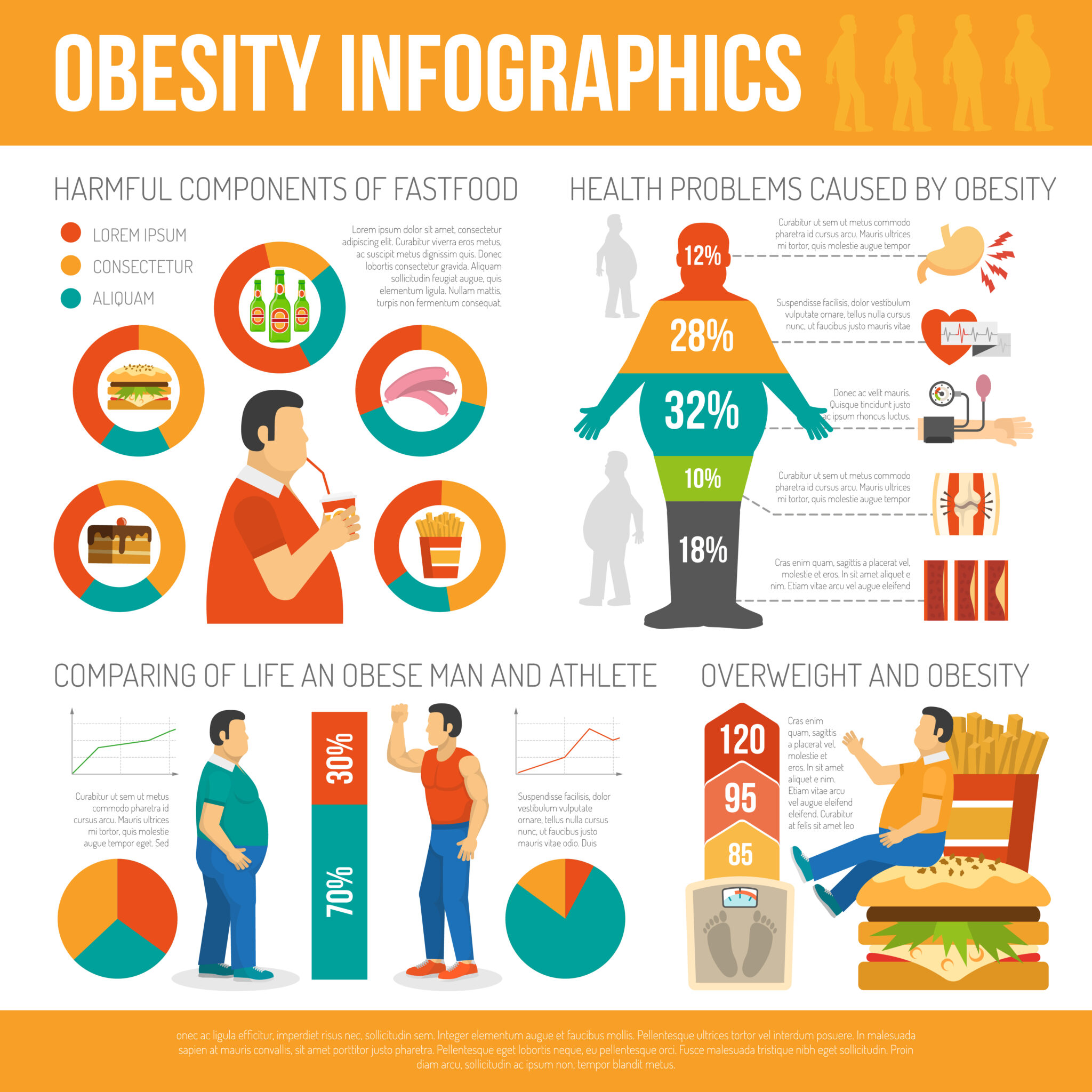 Image by macrovector on Freepik
Image by macrovector on Freepik
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is obesity, and how is it defined?
- Obesity is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of excessive body fat. It is typically defined using the Body Mass Index (BMI), with a BMI of 30 or higher indicating obesity.
2. How prevalent is obesity on a global scale?
- Obesity rates have tripled worldwide since 1975, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). It is a growing epidemic affecting millions of people.
3. What are the health implications of obesity?
- Obesity is associated with a range of serious health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, joint problems, depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
4. What factors contribute to obesity?
- Obesity has multiple causes, including genetic factors, environmental influences (such as a sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy diet), and psychological factors (like emotional eating and stress).
5. How does childhood obesity differ from adult obesity?
- Childhood obesity is a significant concern as it sets the stage for lifelong health challenges. Factors contributing to childhood obesity include lack of physical activity, unhealthy diets, and parental influence.
6. What role does society play in the obesity epidemic?
- Society has a significant impact on obesity through stigmatization and discrimination of obese individuals, economic burdens, and media influences promoting unrealistic body standards.
7. What can individuals do to prevent obesity?
- Preventing obesity involves maintaining a healthy diet, controlling portion sizes, engaging in regular physical activity, and participating in educational programs and community initiatives.
8. What medical treatments are available for obesity?
- Medical treatments include diet and exercise programs under medical supervision, pharmacotherapy (medications for weight loss), and bariatric surgery in some cases.
9. Are there psychological interventions for obesity?
- Yes, psychological interventions like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), mindfulness-based approaches, and support groups can help individuals address emotional aspects related to obesity.
10. How can governments address the obesity epidemic?
- Governments can implement policies and regulations related to food advertising, labeling, and access to unhealthy foods. Sugar taxes and school lunch programs are also initiatives aimed at curbing obesity.
11. What does the future hold for obesity management and research?
- The future of obesity management includes emerging research in genetics, metabolism, and behavioral science, as well as technological solutions like wearable fitness trackers and personalized medicine approaches.
12. Are there real-life success stories of individuals overcoming obesity?
- Yes, the article includes case studies and notable success stories to provide inspiration and insights into effective strategies for weight management.
13. How can individuals contribute to combating the obesity epidemic on a personal level?
- Individuals can make a difference by adopting healthier lifestyle choices, promoting awareness of obesity-related issues, and supporting policies that encourage better nutrition and increased physical activity.
These FAQs provide a snapshot of the comprehensive information covered in the article on obesity. Readers can refer to the article for more in-depth knowledge and insights on this critical health issue.































